Byzantine-robust Federated Learning via Proactive Alarming
>>> Code is available at https://github.com/AISIGSJTU/Siren
Abstract
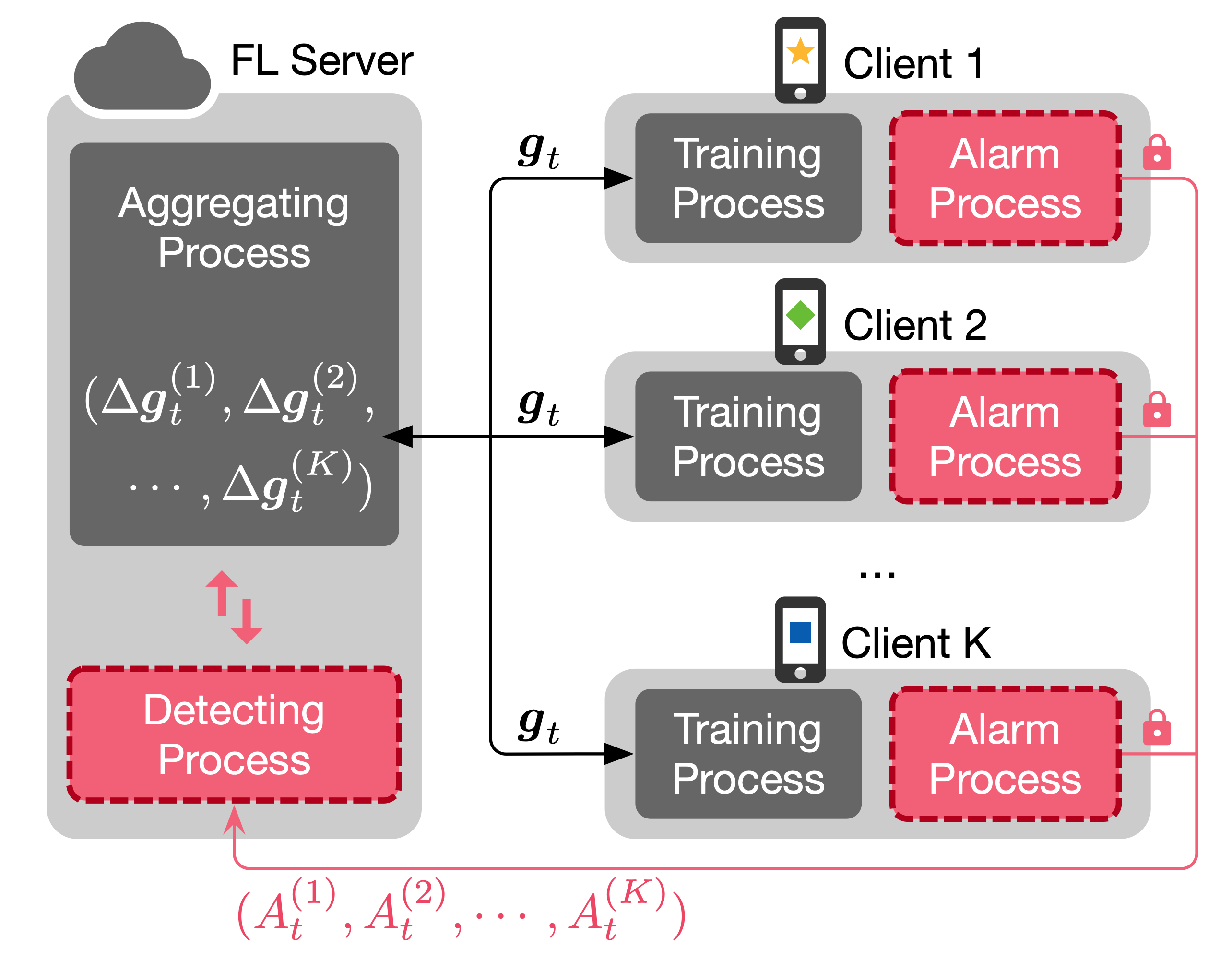
With the popularity of machine learning on many applications, data privacy has become a severe issue when machine learning is applied in the real world. Federated learning (FL), an emerging paradigm in machine learning, aims to train a centralized model while distributing training data among a large number of clients in order to avoid data privacy leaking, which has attracted great attention recently. However, the distributed training scheme in FL is susceptible to different kinds of attacks. Existing defense systems mainly utilize model weight analysis to identify malicious clients with many limitations. For example, some defense systems must know the exact number of malicious clients beforehand, which can be easily bypassed by well-designed attack methods and become impractical for real-world scenarios. This paper presents Siren, a Byzantine-robust federated learning system via a proactive alarming mechanism. Compared with current Byzantine-robust aggregation rules, Siren can defend against attacks from a higher proportion of malicious clients in the system while keeping the global model performing normally. Extensive experiments against different attack methods are conducted under diverse settings on both independent and identically distributed (IID) and non-IID data. The experimental results illustrate the effectiveness of Siren comparing with several state-of-the-art defense methods.