Mitigating Cold-starts in Serverless Computing
——Accepted by the ACM ASPLOS 2024, [PDF]
Abstract
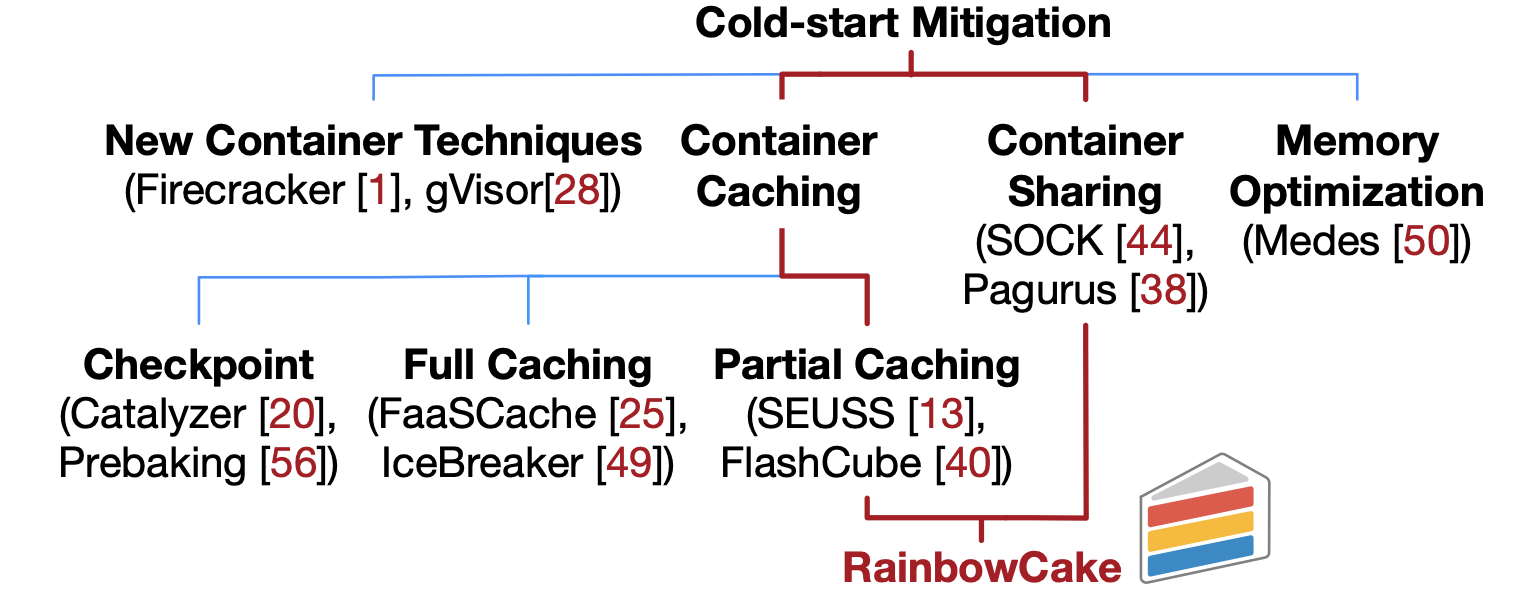
Serverless computing has grown rapidly as a new cloud computing paradigm that promises ease-of-management, cost-efficiency, and auto-scaling by shipping functions via self-contained virtualized containers. Unfortunately, serverless computing suffers from severe cold-start problems—starting containers incurs non-trivial latency. Full container caching is widely applied to mitigate cold-starts, yet has recently been outperformed by two lines of research: partial container caching and container sharing. However, either partial container caching or container sharing techniques exhibit their drawbacks. Partial container caching effectively deals with burstiness while leaving cold-start mitigation halfway; container sharing reduces cold-starts by enabling containers to serve multiple functions while suffering from excessive memory waste due to over-packed containers.
This paper proposes RainbowCake, a layer-wise container pre-warming and keep-alive technique that effectively mitigates cold-starts with sharing awareness at minimal waste of memory. With structured container layers and sharing-aware modeling, RainbowCake is robust and tolerant to invocation bursts. We seize the opportunity of container sharing behind the startup process of standard container techniques. RainbowCake breaks the container startup process of a container into three stages and manages different container layers individually. We develop a sharing-aware algorithm that makes event-driven layer-wise caching decisions in real-time. Experiments on OpenWhisk clusters with real-world workloads show that RainbowCake reduces 68% function startup latency and 77% memory waste compared to state-of-the-art solutions.